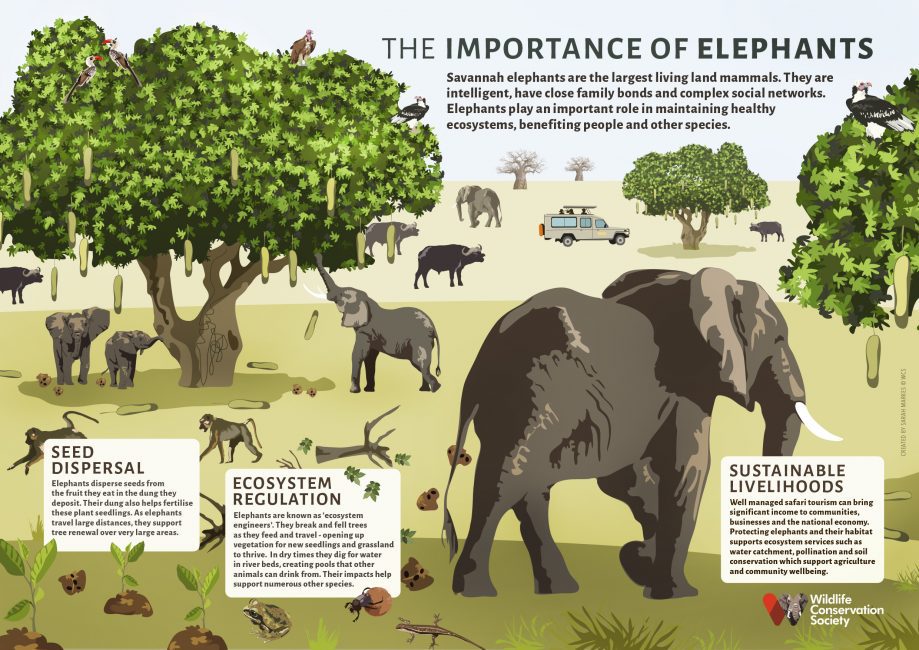
The African elephant, a symbol of the continent’s wildlife, faces extinction due to poaching and habitat loss, with populations plummeting to around 415,000. Efforts to conserve these giants include anti-poaching initiatives, community involvement, and the restoration of habitats. Organizations are now employing modern technology, like GPS tracking and social media campaigns, to raise awareness and combat illegal activities. Successful strategies involve empowering local communities and establishing legal frameworks for protection, contributing to ecological balance. While challenges persist, concerted global efforts offer hope for the future of African elephants, crucial for sustaining ecosystems and intertwining human and wildlife prosperity.
The Last of the Giants: Conservation Efforts to Protect the African Elephant
As dawn breaks over the vast savannah of Africa, the golden rays of the sun illuminate an iconic silhouette against the horizon: the majestic African elephant. Known for their sheer size, complex social structures, and incredible memories, these gentle giants have roamed the continent for millions of years. However, today, the African elephant stands on the precipice of extinction. The dual threats of poaching and habitat loss have led to a significant decline in elephant populations, prompting a concerted global effort to protect these magnificent creatures. This article explores the intricate tapestry of conservation efforts aimed at ensuring the survival of the African elephant and highlights the vital role they play in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitats.
The Elephant Crisis
Population Decline
Once numbering in the millions, African elephant populations are now estimated to be around 415,000, with some regions witnessing a staggering decline of up to 60% in just a few decades. The primary culprits behind this alarming trend are illegal poaching for ivory and the encroachment of human activities that fragment their habitats. In countries like Tanzania and Mozambique, where ivory markets remain a lucrative source of income, elephants have become prime targets for poachers. The demand for ivory, particularly in Asia, fuels this horrific trade, often leading to the brutal killing of entire herds.
Habitat Loss
In addition to poaching, habitat loss due to agricultural expansion, urbanization, and infrastructure development poses a significant threat to the survival of elephants. As forests and grasslands are cleared to make way for human settlements and farming, elephants are forced into smaller and more fragmented areas, leading to conflicts with local communities. This not only jeopardizes the elephants’ survival but also impacts human livelihoods, as elephants sometimes raid crops in search of food.
Conservation Initiatives
Anti-Poaching Efforts
To combat the rise in poaching, various organizations and governments have deployed anti-poaching units equipped with advanced technology and extensive training. These dedicated rangers patrol the vast wilderness areas where elephants roam, utilizing drones, GPS tracking, and surveillance cameras to monitor movements and deter poachers. In 2020, the African Wildlife Foundation established an elite anti-poaching unit in Uganda that focuses on community-based conservation, ensuring local communities are involved in protecting elephants rather than viewing them as threats.
Community Involvement
Empowering local communities is at the heart of many conservation strategies. Initiatives that educate communities about the ecological significance of elephants and involve them in conservation efforts have shown a marked decrease in poaching incidents. For instance, the Amboseli Trust for Elephants in Kenya has successfully integrated community development programs with conservation initiatives, allowing local populations to reap economic benefits from eco-tourism and thus fostering a sense of stewardship.
Legal Frameworks
Influencing policy on both national and international levels is crucial for effective conservation. Organizations like the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) enforce bans on ivory trade, while national governments have established parks and reserves dedicated to elephant protection. As of 2023, countries like Namibia and Botswana have made strides in increasing their elephant populations through well-managed conservation practices and policies that balance ecological responsibilities with community needs.
Habitat Restoration
Restoring elephant habitats is also pivotal for their long-term survival. Projects aimed at reforesting and rehabilitating degraded lands have gained momentum, with NGOs working alongside local governments to restore essential corridors that allow elephants to migrate safely between breeding grounds and feeding areas. The Great Elephant Corridor project in northern Kenya exemplifies this approach, aiming to connect fragmented parks to ensure the free movement of elephants and other wildlife.
The Role of Technology
Innovative Solutions
Technology plays an increasingly vital role in conservation efforts. From GPS collars that track elephant movements to artificial intelligence algorithms that analyze poaching patterns, technological advancements are transforming the way conservationists protect these animals. Innovations like bioacoustic monitoring systems, which use sound recordings to detect illegal activities in remote areas, are crucial for real-time monitoring and quick response actions.
Engaging the Global Community
In an age of connectivity, social media campaigns and digital platforms have exponentially increased awareness about the plight of the African elephant. Initiatives like #StandWithElephants and #SaveTheElephants have mobilized global audiences, urging individuals to support conservation efforts through donations, advocacy, and education. Virtual tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic has also provided an opportunity for people worldwide to engage with African wildlife and contribute to conservation funds.
The Future of African Elephants
The path forward for African elephant conservation is fraught with challenges yet filled with hope. As nations recognize the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the profound ecological roles played by elephants, efforts to secure their survival are gaining momentum. Continued collaboration between governments, NGOs, communities, and the global citizenry will be essential in curbing poaching and preserving habitats.
The African elephant’s story is not simply one of tragedy but also of resilience and potential recovery. For each elephant saved, entire ecosystems flourish, reconnecting the threads of life that sustain not only wildlife but also human communities. The legacy of the African elephant is intertwined with the prosperity of our planet; thus, the responsibility to protect these gentle giants lies with us all.
Conclusion
In this age of environmental upheaval, the fight to protect the African elephant symbolizes a struggle larger than any single species. It exemplifies the intertwined destinies of nature and humanity. As we stand at the threshold of a potential ecological crisis, we must rally together to ensure that the last of the giants do not fade into memory but instead continue to roam freely across the sun-kissed plains of Africa. It is not just about saving a species; it is about safeguarding a future where the wild majesty of the African elephant can thrive for generations to come.